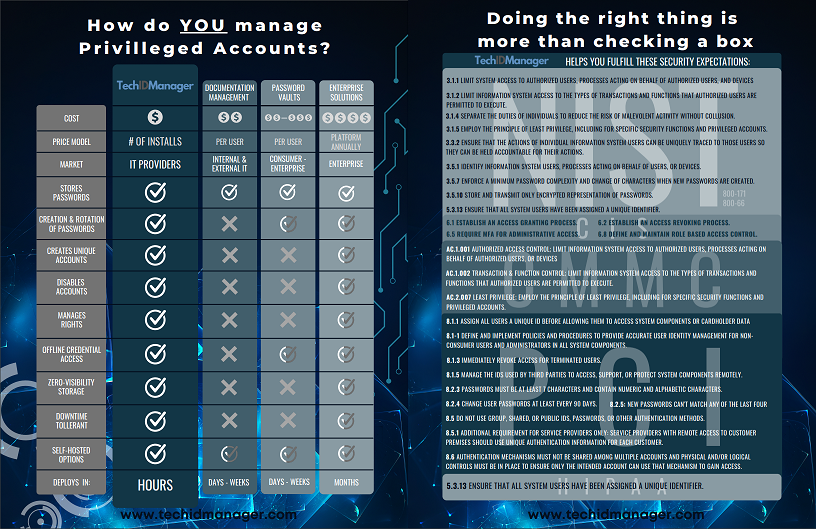
MSPs commonly attempt to ensure cybersecurity compliance with documentation tools, password vaults, and privileged access tools. These tools have their place and should be used by MSPs, but they do not address the core items in every cybersecurity framework like TechIDManager, the Privileged Account Management (PAM) tool designed specifically for MSPs.
NOTE: Using TechIDManager satisfies all of the cybersecurity compliance objectives listed below. The objectives in bold are only accomplished by using TechIDManager when compared to other documentation and password vault tools commonly used by MSPs.
| Objective | Objective Description |
NIST 800-171 |
|
| 3.1.1 | Limit system access to authorized users, processes acting on behalf of authorized users, and devices (including other systems.) |
| 3.1.2 | Limit information system access to the types of transactions and functions that authorized users are permitted to execute. |
| 3.1.4 | Separate the duties of individuals to reduce the risk of malevolent activity without collusion. |
| 3.1.5 | Employ the principle of least privilege, including for specific security functions and privileged accounts. |
| 3.3.2 | Ensure that the actions of individual information system users can be uniquely traced to those users so they can be held accountable for their actions. |
| 3.5.1 | Identify information system users, processes acting on behalf of users, or devices. |
| 3.5.7 | Enforce a minimum password complexity and change of characters when new passwords are created. |
| 3.5.10 | Store and transmit only encrypted representation of passwords. |
NIST 800-53 |
|
| 3.7 | Access Enforcement Role-based Access Control; Enforce a role-based access control policy over defined subjects and objects and control access based upon [Assignment: organization-defined roles and users authorized to assume such roles]. |
NIST 800-66 |
|
| 5.3.1.3 | Ensure that all system users have been assigned a unique identifier. |
CIS Control |
|
| 4.7 | Manage default accounts on enterprise assets and software |
| 5.2 | Use unique passwords. |
| 5.4 | Restrict administrator privileges to dedicated administrator accounts. |
| 5.6 | Centralized account management. |
| 6.1 | Establish an access granting process. |
| 6.2 | Establish an access revoking process. |
| 6.8 | Define and maintain role based access control. |
| 8.2 | Collect audit logs |
| 8.5 | Collect detailed audit logs |
| 8.10 | Retain audit logs |
CMMC |
|
| AC.1.001 | Authorized Access Control: Limit information system access to authorized users, processes acting on behalf of authorized users, or devices (including other information systems.) |
| AC.1.002 | Transaction & Function Control: Limit information system access to the types of transactions and functions that authorized users are permitted to execute. |
| AC.2.007 | Least Privilege: Employ the principle of least privilege, including for specific security functions and privileged accounts. |
PCI |
|
| 8.1.1 | Define and implement policies and procedures to provide accurate user identity management for non-consumer users and administrators in all system components. |
| 8.1.3 | Immediately revoke access for terminated users. |
| 8.1.4 | Remove or disable inactive user accounts within 90 days. |
| 8.1.5 | Manage the IDs used by third parties to access, support, or protect system components remotely. |
| 8.2.3 | Passwords must be at least seven characters and contain numeric and alphabetic characters. |
| 8.2.4 | Change user passwords at least every 90 days. |
| 8.2.5 | Do not allow a new password to be created that is the same as any of the last four passwords used. |
| 8.5 | Do not use group, shared, or public IDs, passwords, or other authentication methods. |
| 8.5.1 | Additional requirement for service providers only: service providers with remote access to customer premises should use unique authentication information for each customer. |
| 8.6 | Authentication mechanisms must not be shared among multiple accounts and physical and/or logical controls must be in place to ensure only the intended account can use that mechanism to gain access. |
Essential Eight Maturity Model |
|
| Level 2 | Restrict Administrative Privileges; Credentials for local administrator accounts and service accounts are long, unique, unpredictable and managed. |
| Level 2 | Restrict Administrative Privileges; Privileged access events are logged. |
| Level 2 | Restrict Administrative Privileges; Privileged account and group management events are logged. |
| Level 3 | Restrict Administrative Privileges; Privileged access to systems and applications is limited to only what is required for users and services to undertake their duties. |
| Level 3 | Restrict Administrative Privileges; Privileged access events are centrally logged. |
| Level 3 | Restrict Administrative Privileges; Privileged account and group management events are centrally logged. |
| Level 3 | Restrict Administrative Privileges; Event logs are protected from unauthorised modification and deletion. |
HIPAA |
|
| 164.312 (a)(2)(i) | Unique user identifier. |
There are other cybersecurity frameworks that TechIDManager helps with that are not listed here in detail. Contact us for specifics on any other cybersecurity framework.
Download the Cybersecurity Frameworks Compliance Objectives White Paper